What is GPON?
GPON stands for Gigabit Passive Optical Networks. GPON is a point-to-multipoint access mechanism. Its main characteristic is the use of passive splitters in the fiber distribution network, enabling one single feeding fiber from the provider’s central office to serve multiple homes and small businesses.
What Is XG(S)-PON?
XG(S)-PON is evolved from the existing GPON technology, the XG-PON is with the bandwidth of 10G for downstream and 2.5G for upstream, XGS-PON with the bandwidth of 10G for downstream and 10G for upstream. XGS-PON is a higher bandwidth, symmetric version of GPON. Again, the same capabilities of GPON and can co-exist on the same fiber with GPON.
Specification Differences Among GPON, XG-PON and XGS-PON
| Specifications | GPON | 10G GPON | |
| XG-PON | XGS-PON | ||
| Network Structure | 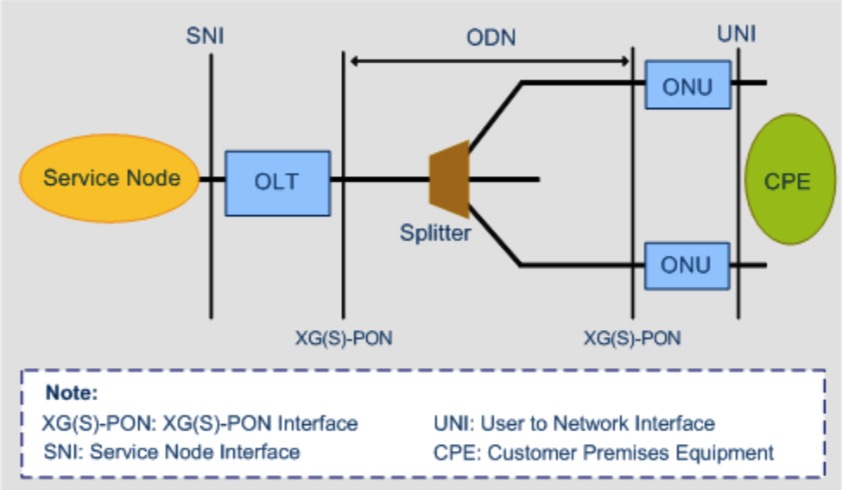 |
||
| Wavelength | Downstream: 1480 ~ 1500 nm
Upstream: 1290 ~ 1330 nm |
Downstream: 1575 ~ 1580 nm
Upstream: 1260 ~ 1280 nm |
Downstream: 1575 ~ 1580 nm
Upstream: 1260 ~ 1280 nm |
| Center wavelength | Downstream: 1490 nm
Upstream: 1310 nm |
Downstream: 1577 nm
Upstream: 1270 nm |
Downstream: 1577 nm
Upstream: 1270 nm |
| Max. Line Rate | Downstream: 2.488 Gbit/s
Upstream: 1.244 Gbit/s |
Downstream: 9.953 Gbit/s
Upstream: 2.488 Gbit/s |
Downstream: 9.953 Gbit/s
Upstream: 9.953 Gbit/s |
| Frame Structure | GEM | XGEM | XGEM |
| Max. Physical Transmission Distance | 60 km | 100 km | 100 km |
| Max. Split Ratio | 1:128 | 1:256 | 1:256 |