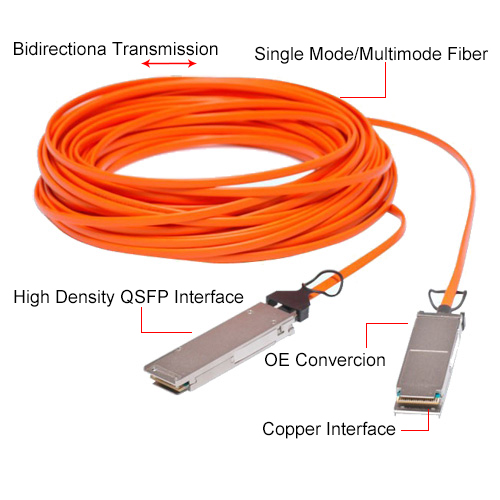
The small factor pluggable Transceivers (SFP28 Transceivers) is an optical module transceivers used for both telecommunication and data communication applications. The TARLUZ SFP28 is a high performance transceiver module for up to 25x Gigabit Ethernet data links over a single fibre pair. The maximum reach is 10km. This transceiver module is compliant with the SFP+ Multisource Agreement (MSA).
What does SFP28 short for?
SFP28 is abbreviation of Small Form-Factor Pluggable 28. It is the third generation of the SFP interconnect systems designed for 25G performance per the IEEE 802.3by specification (25GBASE-CR).
What is the maximum supported distance for 25G Transceivers and Cables?
The maximum currently supported distance for 25G is 10km with SFP-25G-LR product. Additional optics may be released in the future to support longer distances.
What is the difference between SFP28 and SFP+?
The pinouts of SFP28 and SFP+ connectors are mating compatible. However, SFP+ is designed to operate at 10.3125 Gb/s whereas SFP28 is designed to operate at 25.78125 Gb/s. SFP28 has increased bandwidth, superior impedance control and less crosstalk than the SFP+ solution. Also, the SFP28 copper cable has significantly greater bandwidth and lower loss when compared to the SFP+ version.
Can I use SFP28 modules in SFP+ ports?
Yes, SFP28 is backwards compatible with SFP+ ports and will work sufficiently. SFP+ cables can be plugged into SFP28 ports but they are not designed for 25Gb/s data rates.
Do you offer custom EEPROM programming?
Yes, upon request. Cables with custom EEPROMs will be supplied under a different part number.
Do these products support 25G per lane data rate and for what standards?
Yes, per SFF-8402, SFF-8419, SFF-8432, SFF-8472 and IEEE 802.3by, these cables support 25G Ethernet.
Do you have design qualification test data?
TARLUZ’s performance testing exceeds industry requirements. Mechanical and electrical test data is available upon request.
Where are these cable assemblies used?
These are « point-to-point » cables that are used to directly connect two pieces of active network equipment like switch-to-switch or switch-to-server applications They are most commonly used in data centers for ToR (top of rack) or MoR (middle of rack) switch applications.