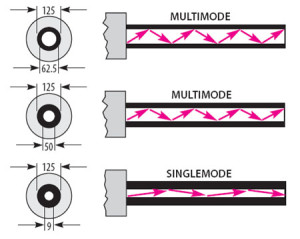
In terms of physical properties, the difference between these two fiber types is the diameter of the core—the light-carrying region of the fiber. In 62.5/125 fiber, the core has a diameter of 62.5 microns and the cladding diameter is 125 microns. For 50/125, the core has a diameter of 50 microns with the same cladding diameter. The diameter measurement of the fiber core has an inverse relationship to the effective bandwidth and the distance limitations of the fiber. As the core size decreases, the bandwidth and distance capabilities increase.
Bandwidth, or information-carrying capacity, is specified as a bandwidth-distance relationship with units of MHz-km (megahertz over one kilometer). The bandwidth needed to support an application depends on the data rate of transmission. As the bandwidth (MHz) goes up, the distance that bandwidth can be transmitted (km), goes down. A high-bandwidth fiber can transmit more information for longer distances.
While 62.5-micron/ISO OM1 fiber has been the most common multimode optical cable used in local area network applications, 50-micron/ISO OM3 fiber is the standard for storage area networks and their Fibre Channel data link connectivity. The 50-micron/ISO OM2/OM3 fiber was chosen because it supports longer Fibre Channel cabling distances (such as 150 m at 400 Mbps using short wave length 850 nm optics) when compared with 62.5-micron/ISO OM1. This is also true for Gigabit Ethernet (600 m) and exceeds the computer room objective of 100 meters for the 10GBASE-T standard finalized in June 2006. The increased information-carrying ability and adoption for SAN/Fibre Channel usage within data centers has changed the design recommendation to laser optimized 50-micron/ISO OM3 fiber throughout the data center. One such IDC design envisions Ethernet and Fibre Channel distribution switches sitting between server cabinet rows and SAN equipment, providing any-to-any configuration capabilities and a migration path to all optical networking within the data center.