Features:
- Low cost: SR8 is the cost optimized 400G end to end solution for greenfield new install/ brownfield upgrade for <50m
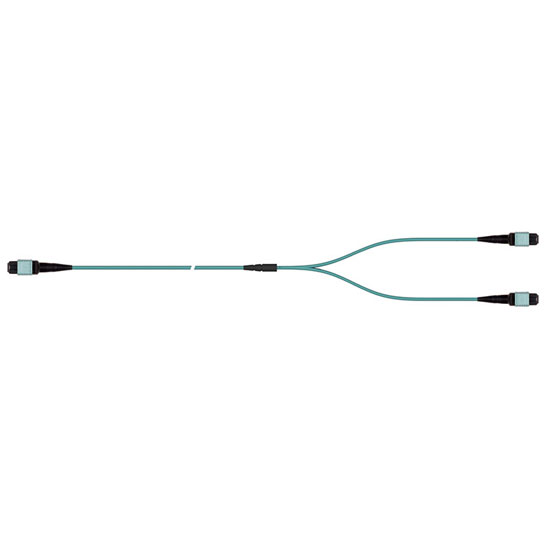 reach.
reach. - Flexibility: 400G-SR8 offers flexibility of fiber shuffling with 50G/100G/200G configurations. It also supports breakout at different speeds for various applications: compute, storage, flash, GPU, and TPU.
- High density: 400G-SR8 OSFP/QSFP DD transceiver can be used as 400GBASE-SR8, 2x200GBASE-SR4, 4x100GBASE-SR2, 8x50GBASE-SR
- Backward compatibility: Compatible optical specifications (850nm wavelength, receiver sensitivity, etc) with 100GBASE-SR4 and 40GBASE-SR4. Compatible with existing MPO-12 fiber plant through use of break-out cable.
- Reach: Same reach as 100GBASE-SR4: 70m OM3, 100m OM4.
- Fast time to market: All components (850nm 50G PAM4 VCSEL, MPO16)are ready.
ToR to Leaf: Flexible BW with Better Fault Tolerance
8-lane MMF enables flexible BW between switches in green field (new install)
| Per port in TOR | Per port in Leaf switch | Cable Implementation Example |
| 1x400GbE | 1x400GbE | MPO16 at switch <-> MPO16 at patch panel |
| 2x200GbE | 2x200GbE | Shuffle cable: MPO16 at switch port, MPO16/MPO32 at patch panel |
| 4x100GbE | 4x100GbE | Shuffle cable: MPO16 at switch port, MPO16/MPO32 at patch panel |
| 2x200GbE | 200GbE | MPO-16 break-out to two MPO-12 cables (octopus) |
8-lane MMF design allows maximum port density and maximum efficiency in brown field upgrade.
| Per port in TOR | Per port in Leaf switch | Cable Implementation Example |
| 2x100GbE (8x25G NRZ) | 1x100GbE (4x25G NRZ) | Breakout cable: MPO16 at TOR <-> 2xMPO8 at patch panel |
| 2x40GbE (8x10G NRZ) | 1x40GbE (4x10G NRZ) | Breakout cable: MPO16 at TOR <-> 2xMPO8 at patch panel |
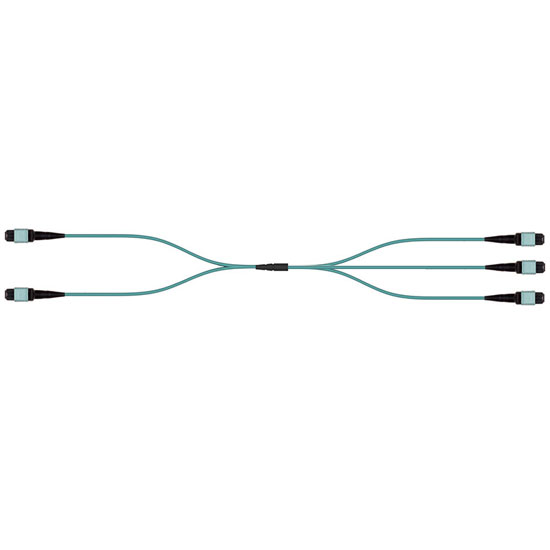
ToR/Switch to Server Breakout Topology
- Optical connection between TOR/S1 switch and servers provides flexible bandwidth to server and solve the mismatch between network ports and server ports.
- Different application required different server BW, from 50GbE to 200GbE/400GbE
- 8-lane MMF applications: break out to IEEE lower speed interfaces:
- 8x 50GBASE-SR: MPO16 to 8xLC
- 4x 100GBASE-SR2 (2×50): MPO 16 to 2xMPO8
- 2x 200GBASE-SR4 (4×50): MPO 16 to 2xMPO8
- 2x 100GBASE-SR4 (4×25): MPO 16 to 2xMPO8
- AOC could be an option, but deployment is difficult especially when one server connects to multiple switches.
Technical feasibility
- 100m OM3 reach with KP4 FEC (2e-4) has been demonstrated with PAM4 VCSEL and 25G NRZ VCSEL.
- Leverage 50GbE Electrical I/O specification.
- Define optical specification for 400G-SR8
Summary
- 400GBASE-SR8 has distinct identity from SR16 and supports applications not supported by SR4.2
- For 400GbE switch to switch connections, SR8 operates over a lower cost and more user-friendly MMF cable than SR16. It offers better network port utilization
- 400GBASE-SR8 specification would permit implementers to design one module offering breakout capability to support 50G/100G/200G connections
- This is no different than 40GBASE-SR4, and 100GBASE-SR4 which were all used for break-out and shuffle, with IEEE standard only specifying point to point link. These were very successful IEEE MMF standards.
- Technical feasibility has been demonstrated.






