- Home
- Products
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Outdoor Cable
- ADSS Cable
- All Dielectric Self-supporting Aerial Cable ADSS
All Dielectric Self-supporting Aerial Cable ADSS
- General Details
- Features
- Specifications
- Applications
The fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads (fiber core), each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves. featured with the following advantages compared with traditional copper cable: Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth to carry data than copper cables. Fiber optic cables are less susceptible than copper cables to interference. Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than copper wires.
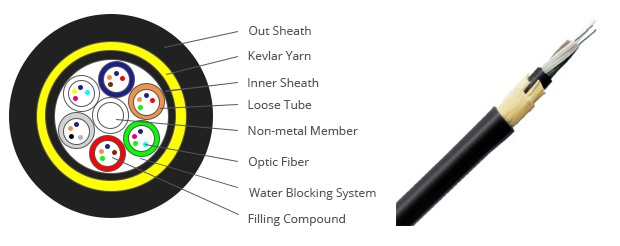
The 250um bare fibers are positioned into a loose tube made of high modulus plastics. The tubes are filled with a water-resistant filling compound. The tubes (and fillers) are stranded around a FRP (Fiber Reinforced Plastic) as a non-metallic central strength member into a compact and circular cable core. After the cable core is filled with filling compound. it is covered with thin PE (polyethylene) inner sheath. After stranded layer of Aramid yarns are applied over the inner sheath as strength member, the cable is completed with PE or AT (anti-tracking) outer sheath.
Installation method
Aerial
Standards
YD/T901-2009
IEEE P 1222
IEC 60794-1
- Can be installed without shutting off the power
- Excellent AT performance, The maximum inductive at the operating point of AT sheath can reach 25kV
- Light weight and small diameter reducing the load caused by ice and wind and the load on towers and backprops
- Large span lengths and the largest span is over 1000m
- Good performance of tensile strength and temperature
- The design life span is 30 years
Transmission Characteristics
| G.652 | G.655 | 50/125μm | 62.5/125μm | ||
| Attenuation (+20℃) |
@850nm | ≤3.0 dB/km | ≤3.0 dB/km | ||
| @1300nm | ≤1.0 dB/km | ≤1.0 dB/km | |||
| @1310nm | ≤0.36 dB/km | ≤0.40 dB/km | |||
| @1550nm | ≤0.22 dB/km | ≤0.23dB/km | |||
| Bandwidth (Class A) | @850nm | ≥500 MHz·km | ≥200 MHz·km | ||
| @1300nm | ≥1000 MHz·km | ≥600 MHz·km | |||
| Numerical Aperture | 0.200±0.015NA | 0.275±0.015NA | |||
| Cable Cut-off Wavelengthλcc | ≤1260nm | ≤1480nm | |||
| Ref. outer diameter (mm) | Ref. weight (kg/km) | Ref.daily max.working tension (KN) | Max allowable working tension kN | Break strength (KN) | Strength member CSA (mm2) | Modulus of elasticity kN/ mm2 | Heat expansion coefficient×10-6/k | Ref. outer diameter | Suitable span | ||||
| PE sheath | AT sheath | A | B | C | D | ||||||||
| 12.5 | 125 | 136 | 1.5 | 4 | 10 | 4.6 | 7.6 | 1.8 | 12.5 | 160 | 100 | 140 | 100 |
| 13 | 132 | 142 | 2.25 | 6 | 15 | 7.6 | 8.3 | 1.5 | 13 | 230 | 150 | 200 | 150 |
| 13.3 | 137 | 148 | 3 | 8 | 20 | 10.35 | 9.45 | 1.3 | 13.3 | 300 | 200 | 290 | 200 |
| 13.6 | 145 | 156 | 3.6 | 10 | 24 | 13.8 | 10.8 | 1.2 | 13.6 | 370 | 250 | 350 | 250 |
| 13.8 | 147 | 159 | 4.5 | 12 | 30 | 14.3 | 11.8 | 1 | 13.8 | 420 | 280 | 400 | 280 |
| 14.5 | 164 | 177 | 5.4 | 15 | 36 | 18.4 | 13.6 | 0.9 | 14.5 | 480 | 320 | 460 | 320 |
| 14.9 | 171 | 185 | 6.75 | 18 | 45 | 22 | 16.4 | 0.6 | 14.9 | 570 | 380 | 550 | 380 |
| 15.1 | 179 | 193 | 7.95 | 22 | 53 | 26.4 | 18 | 0.3 | 15.1 | 670 | 460 | 650 | 460 |
| 15.5 | 190 | 204 | 9 | 26 | 60 | 32.2 | 19.1 | 0.1 | 15.5 | 750 | 530 | 750 | 510 |
| 15.6 | 194 | 208 | 10.5 | 28 | 70 | 33 | 19.6 | 0.1 | 15.6 | 800 | 560 | 800 | 560 |
| 16.3 | 211 | 226 | 12.75 | 34 | 85 | 40 | 20.1 | 0.1 | 16.3 | 880 | 650 | 880 | 650 |
| 16.8 | 226 | 242 | 15.45 | 41 | 103 | 48 | 24 | -0.4 | 16.8 | 1000 | 750 | 1000 | 760 |
| 17.2 | 236 | 253 | 16.2 | 45 | 108 | 51 | 25.1 | -0.5 | 17.2 | 1100 | 800 | 1100 | 830 |
| 17.9 | 249 | 266 | 18 | 50 | 120 | 58.8 | 26.1 | -0.8 | 17.9 | 1180 | 880 | 1180 | 900 |
- FTTH Network GPON, EPON.
- Rural communication
- Local trunk line
- CATV
- Computer networks system