- Home
- Products
- Fiber Optic Cable
- Outdoor Cable
- Stranded Loose Tube Cable
- Stranded loose tube single armored single jacket cable GYTS
Stranded loose tube single armored single jacket cable GYTS
- General Details
- Features
- Specifications
- Applications
The fiber optic cable consists of a bundle of glass threads (fiber core), each of which is capable of transmitting messages modulated onto light waves. featured with the following advantages compared with tranditional copper cable: Fiber optic cables have a much greater bandwidth to carry data than copper cables. Fiber optic cables are less susceptible than copper cables to interference. Fiber optic cables are much thinner and lighter than copper wires.
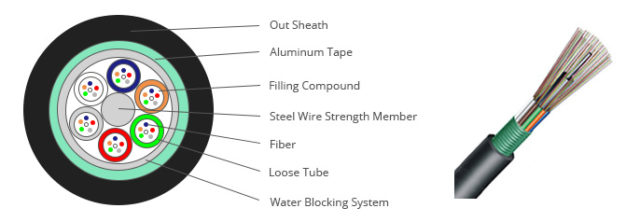
The 250um bare fiber are positioned in a loose tube made of a high modulus plastic. The tubes are filled with a water-resistant filling compound. central strength member (sometimes sheathed with polyethylene (PE) for high count fiber optic cable). Tubes (and fillers) are stranded around the strength member into a compact and circular cable core. The PSP is longitudinally applied over the cable core, which is filled with the filling compound to protect it from water ingress. The cable is completed with a PE sheath.
Installation method
Aerial, Duct and direct burial.
Standards
YD/T901-2009
IEC 60794-1
- Good mechanical and temperature performance
- High strength looes tube that is hydrolysis resistant
- Special tube filling compound ensure a critical protection of fiber
- Crush resistance and flexibility
Transmission Characteristics
| G.652 | G.655 | 50/125μm | 62.5/125μm | ||
| Attenuation (+20℃) |
@850nm | ≤3.0 dB/km | ≤3.0 dB/km | ||
| @1300nm | ≤1.0 dB/km | ≤1.0 dB/km | |||
| @1310nm | ≤0.36 dB/km | ≤0.40 dB/km | |||
| @1550nm | ≤0.22 dB/km | ≤0.23dB/km | |||
| Bandwidth (Class A) | @850nm | ≥500 MHz·km | ≥200 MHz·km | ||
| @1300nm | ≥1000 MHz·km | ≥600 MHz·km | |||
| Numerical Aperture | 0.200±0.015NA | 0.275±0.015NA | |||
| Cable Cut-off Wavelengthλcc | ≤1260nm | ≤1480nm | |||
| Cable Type | Fiber Count | Tubes | Fillers | Cable Diameter (mm) | Cable Weight kg/km | Tensile Strength (N) | Crush Resistance (N/100mm) | Bending Radius mm | |||
| Long Term | Short Term | Long Term | Short Term | Static | Dynamic | ||||||
| GYTS-2~6 | 2~6 | 1 | 4 | 10.3 | 120 | 600 | 1500 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-8~12 | 8~12 | 2 | 3 | 10.3 | 120 | 600 | 1500 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-14~18 | 14~18 | 3 | 2 | 10.3 | 120 | 600 | 1500 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-20~24 | 20~24 | 4 | 1 | 10.3 | 120 | 600 | 1500 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-26~30 | 26~30 | 5 | 0 | 10.3 | 120 | 600 | 1500 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-32~36 | 32~36 | 6 | 0 | 10.7 | 135 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-38~48 | 38~48 | 4 | 1 | 11.3 | 117 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-50~60 | 50~60 | 5 | 0 | 11.3 | 117 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-62~72 | 62~72 | 6 | 0 | 12.0 | 159 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-74~84 | 74~84 | 7 | 1 | 13.7 | 215 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-86~96 | 86~96 | 8 | 0 | 13.7 | 215 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-98~108 | 98~108 | 9 | 1 | 15.5 | 240 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-110~120 | 110~120 | 10 | 0 | 15.5 | 240 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-122~132 | 122~132 | 11 | 1 | 17.3 | 290 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
| GYTS-134~144 | 134~144 | 12 | 0 | 17.3 | 290 | 1000 | 3000 | 300 | 1000 | 10D | 20D |
- FTTH Network GPON, EPON.
- Rural communication
- Local trunk line
- CATV
- Computer networks system