| Attenuation | reduction of the signal magnitude or loss, caused by absorption and scattering Values are normally expressed in decibels (dB) |
| Attenuator | a passive device for reducing the amplitude of a signal without distorting the waveform |
| Bidirectional | a device, which operates in both directions |
| Broadband Device | optical broadband devices cover a wide range of wavelengths |
| Center Wavelength | the nominal operating wavelength of an optical device |
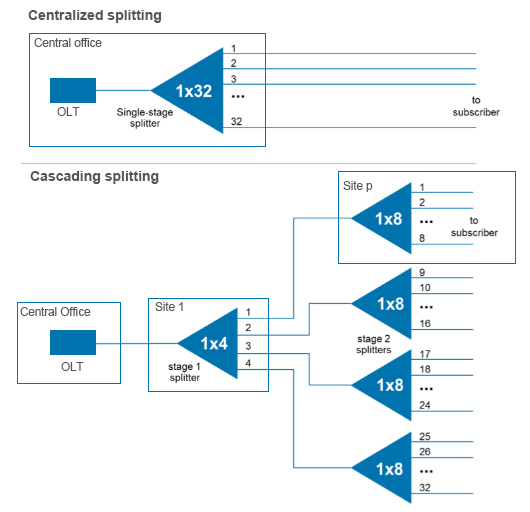
| Coupler | a bidirectional device with three or more fiber ends, combining the signals of two or more input ports into one output port Also referred to as splitter |
| Decibel (dB) | a logarithmic unit of measurement for calculating the attenuation of an optical device or an optical system A change of -3 dB equates to the halving of the optical power |
| Demultiplexer | a device that separates two or more multiplexed signals into its original single signals; the inverse of a multiplexer |
| Directivity | the amount of undesired optical signals observed at a given input port of a device Also referred as near-end crosstalk (NEXT) |
| Dual Window | a passive optical component that is optimised to operate at two different center wavelengths For example at 1310 nm and 1550 nm |
| Excess Loss | attenuation or loss of the optical component itself, without including any attenuation effects of the device due to signal splitting |
| Fused Biconical Tapering (FBT) | a manufacturing process for passive optical network components It consist of twisting bare fibers together, stretching and then fusing the fibers together |
| Insertion Loss (IL) | a sum of excess loss, splitting loss and loss caused by other optical effects Total loss experienced by signal traversing the device |
| Isolation | the amount of undesired optical signals observed at a given output port of a device Also referred as far-end crosstalk (FEXT) |
| Multiplexer | a device that combines two or more signals into a single output; the inverse of a demultiplexer |
| Operating Wavelength | the wavelength, or wavelength range, for which a passive optical component is optimised for operating |
| Planar Lightwave Circuit (PLC) | a manufacturing process for optical passive network components Its main components is a waveguide array that is induced in a silica chip by using a photolithographic masking process |
| Polarization Depen- dent Loss (PDL) | changes in attenuation caused by the state of polarisation (SOP) This optical effect results in a deviation between the maximum and minimum loss on an optical device |
| Return Loss (RL) | the ratio of optical power reflected back along the path of transmission from a connector or any other optical device Values are normally expressed in decibels (dB) |
| Single Window | a passive optical component that is optimised to operate at a single specified center wavelength For example at 1310 nm or 1550 nm |
| Splitter | a bidirectional device with three or more fiber ends, which divides the signal from one input port into two or more output ports Also referred to as coupler |
| Splitting Ratio | the percentage of optical power transferred to an output port of an optical device, with respect to the total power at the input to the device |
| Uniformity | the maximum deviation of insertion loss between the different ports on a device within the operating wavelength range |
| Wavelength Division Multiplexing (WDM) | a technique of transmitting various signals at different wavelengths through the same fiber |