The rapid growth of data-intensive applications such as AI (Artificial intelligence), ML (Machine Learning), HPC (High-performance Computing) and cloud computing. 800G bandwidth is the basic need for those applications, OSFP (Octal Small Form Factor Pluggable) transceivers is one type of form factor for 800G transceivers. The OSFP transceivers are available in two primary designs: finned-top and flat-top, each tailored to specific thermal and spatial requirements. This essay explores the key differences, advantages, and applications of these two designs, providing a comprehensive understanding of their roles in modern networking, and selecting the right type for your network equipment.
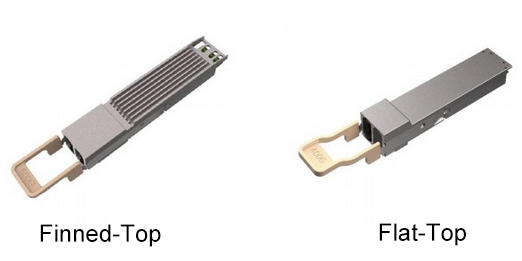
Finned-Top Design: Enhanced Thermal Management
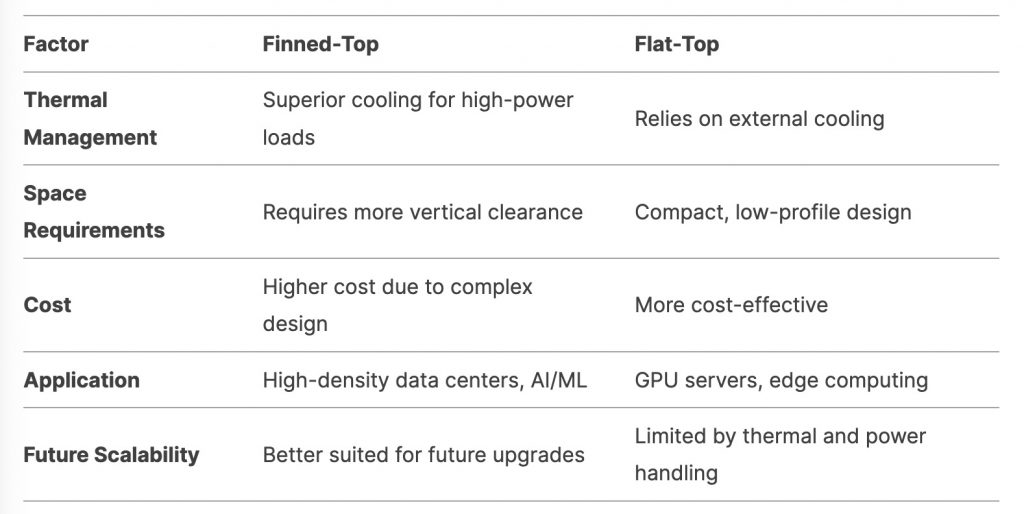
The finned-top design features a heat sink with fins on top of the module, significantly increasing the exterior surface area for better heat dissipation. This design is particularly beneficial in high-density environments where airflow is restricted, such as large-scale data centers and AI-driven applications.
- Superior Cooling: The fins enhance passive cooling, reducing the risk of overheating and ensuring stable performance under heavy workloads.
- High-Power Applications: Finned-top modules are ideal for high-power scenarios, such as NVIDIA Quantum-2 NDR InfiniBand and Spectrum-4 SN5600 Ethernet switches, where effective heat management is critical.
- Space Requirements: While the fins require more vertical space, they provide better airflow management, making them suitable for environments with adequate clearance.
Flat-Top Design: Space Efficiency and Compact Installations
The flat-top design, in contrast, similar to the traditional SFP, QSFP and QSFP-DD transceivers, features a smooth, flat surface without protruding fins. This design is optimized for environments where vertical space is limited, such as edge computing and GPU servers.
- Compact Profile: The low-profile design allows for greater flexibility in tight installations, such as NVIDIA ConnectX-7 adapter cards and DGX H100 GPU links.
- External Cooling**: Flat-top modules rely more on external cooling mechanisms, making them suitable for controlled environments with moderate thermal demands.
- Cost-Effectiveness**: The simpler design of flat-top transceivers reduces manufacturing complexity and costs, making them a budget-friendly option for certain applications.
Applications of Finned-Top vs. Flat-Top OSFP Transceivers
The choice between finned-top and flat-top designs depends on the specific requirements of the application:
Finned-Top: Best suited for high-density data centers, AI workloads, and environments with limited airflow, where superior thermal management is essential.
Flat-Top: Ideal for compact setups, such as GPU servers and edge computing, where space efficiency and moderate cooling are prioritized.